Your LLC must include “limited liability company” or an abbreviation (LLC or L.L.C.) and cannot have words that could confuse your California LLC with any government agency. Your business name also cannot include words like bank, insurance, or university without approval from state authorities.
How to Start Your Own LLC in California
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young has over 25 years of experience in business in various roles, including bank management, marketing management, and business education.
Reviewed by: Sarah Ruddle
For over 15 years, Sarah Ruddle has been a noteworthy leader in the business and nonprofit world.
Updated on January 3, 2025

When starting a new business, one of the first big decisions is which type of business entity to form. Many entrepreneurs choose a limited liability company (LLC) because of its many benefits. An LLC provides personal liability protection, for example, so that your assets are not at risk if your business is sued or cannot pay its debts.
Also, an LLC is a “pass-through entity” in taxes, meaning income passes through the company to the LLC owners or members who report it on their tax returns.
LLCs also offer flexibility in management and tax status, yet another reason it’s popular in California.
Here are the steps that you need to take to form an LLC in California.
If you prefer video content, we offer an extensive visual guide on how to form an LLC in California.

1. Name Your California LLC
Naming your business can be challenging. You need a name that’s unique and easy to remember and conveys what your business does. To choose a name, you can try a few different methods:
- Decide on a Business Concept: Before you name your LLC, you need to have a clear idea of what your business will do.
- Ask People You Know for Suggestions: Reach out to people whose opinions you value and trust. Explain your business concept and ask for their thoughts on a name.
- Do a Web Search: Once you have a few name ideas, check their online presence. Is the domain name available? Are there companies with similar names that could create confusion?
- Use an Online Business Name Generator: They can provide inspiration and help you think about your business from different angles. Keep in mind, though, that these generators can’t replace human creativity and may not understand the nuances of your business as well as you do.
Your business name is your business identity, and the first impression people will have of your company, so be sure to take your time with this step and get it right.
Once you have a few business name ideas, you’ll want to ensure they’re available. First, go to the Business Search page on the Secretary of State website and enter your business name. You should also search for similar business names, as you don’t want a name that can be easily confused with other businesses in California.
Also, check California’s LLC naming regulations to make sure you comply.
Next, check with the US Patent and Trademark Office to ensure the name is not trademarked and is thus available nationally.
Here are additional tips and suggestions provided to assist in the process of choosing a name for a California LLC.
Once you’ve confirmed these, it’s a good idea to reserve the name with the state using its Name Reservation form. To reserve an LLC name in California, visit the Secretary of State’s bizfile Online website. If you don’t already have an account, you will need to register to complete the online name reservation.
Once you create an account, log in and click the Forms link on the left-hand side. Then click the Entity Name Reservation icon. Then, click File Online in the pop-up box.

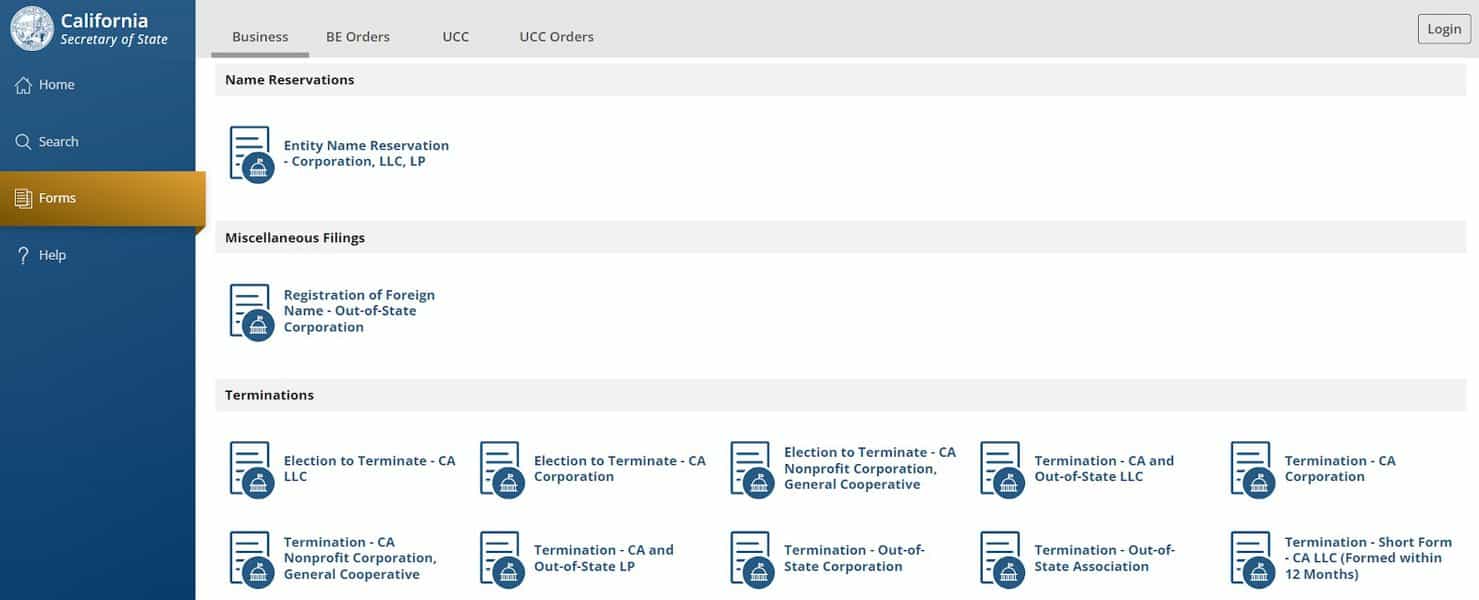
Next, move through the online application and enter the required information on each screen.

Once complete, review your submission to confirm and pay the $10 filing fee.
Once your application is processed, your LLC name will be reserved for 60 days.
If you wish to file by mail, download and submit a paper application along with the filing fee.
Doing Business As (DBA)
You may want to do business under a name other than your LLC name. For this, you’ll need to register a “doing business as,” or DBA name, which is known as a fictitious business name in California. There are two main reasons you might want to use a DBA.
- Suppose you want to add new product lines. For example, if your business name is “JJ’s Waffles,” you want to expand and offer “JJ’s Muffins.” You can have multiple DBAs under the umbrella of your one LLC.
- When you have a DBA, you can have a business bank account under that name. So if you add “JJ’s Muffins,” customers can pay “JJ’s Muffins,” and you can deposit those payments into the bank account with that name.
To register a fictitious business name in California, you’ll need to contact the city, county clerk, and recorder where the principal place of business is. To find your local agency, visit the CalGold Permit Assistance website.
2. Select a Registered Agent
California requires LLCs to appoint a registered agent, a person or company authorized to accept and respond to official business correspondence, such as legal, tax, or financial documents.
The registered agent ensures all necessary notices and documents are received. In California, a registered agent can be an LLC member, individual, or entity that meets state requirements. In California, a registered agent must:
- Be 18 years or older
- Have a physical address in California
- Be available during regular business hours
- Be registered to operate in California, if it’s a business
Many business owners hire a registered agent service to ensure their LLC stays fully compliant and for convenience.
If you choose to be your registered agent, you must be at your registered agent’s address for all business hours. A registered agent service allows you to be wherever you need to be to run and grow your business.
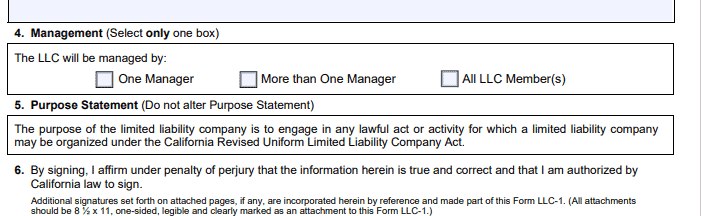
3. Determine Your Management Structure
Members or managers can manage LLCs. In a member-managed LLC, members handle all management duties. In a manager-managed LLC, non-member employees oversee operations and management duties.
Note that with a manager-managed LLC, a member can be a manager, but only in cooperation with another manager who is not a member.
Member-managed LLCs generally work best for LLCs with few members, all of whom can take an active role in day-to-day operations. Conversely, manager-managed LLCs are best for LLCs with multiple members, some of whom want to be “silent” or passive members and not involved in day-to-day operations.
Most LLCs are member-managed, as they are small businesses that cannot afford a management team.
In California, you must specify in your articles of organization whether your LLC will be member-managed or manager-managed.
Discover the difference between member-managed and manager-managed LLCs, and gain insights on selecting the appropriate management structure for your LLC.
4. File Articles of Organization with the California Secretary of State
To start, visit the California Secretary of State website and create an account to access the articles of the organization online.

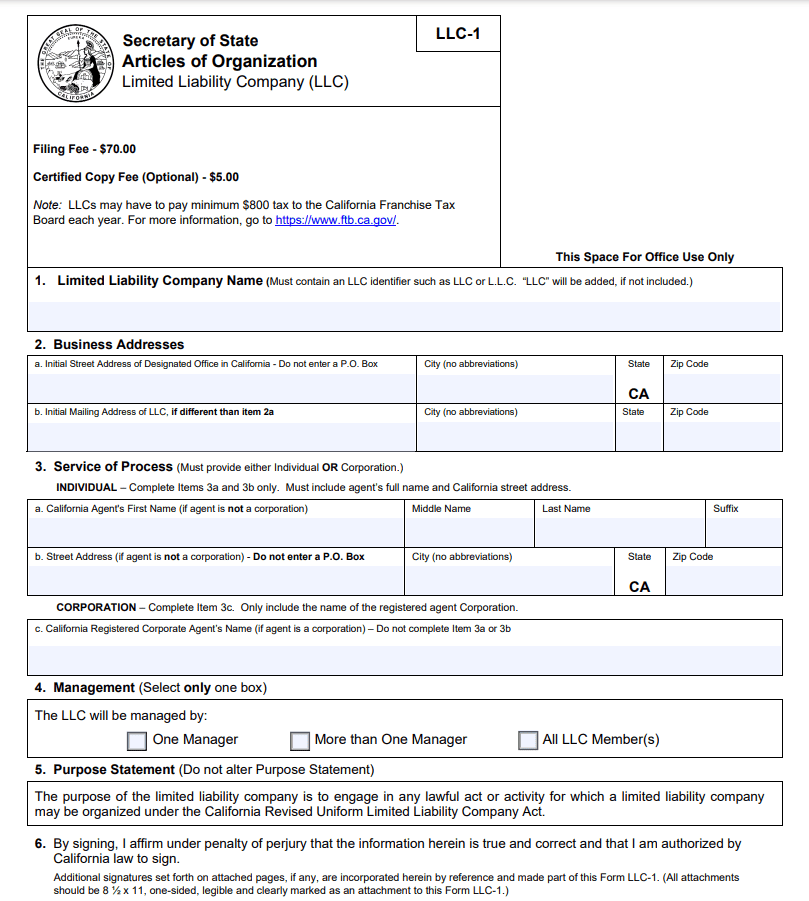
In California, the articles of organization require the following information:
- LLC name
- Principal office address
- Registered agent information
- Registered office address
- Management structure

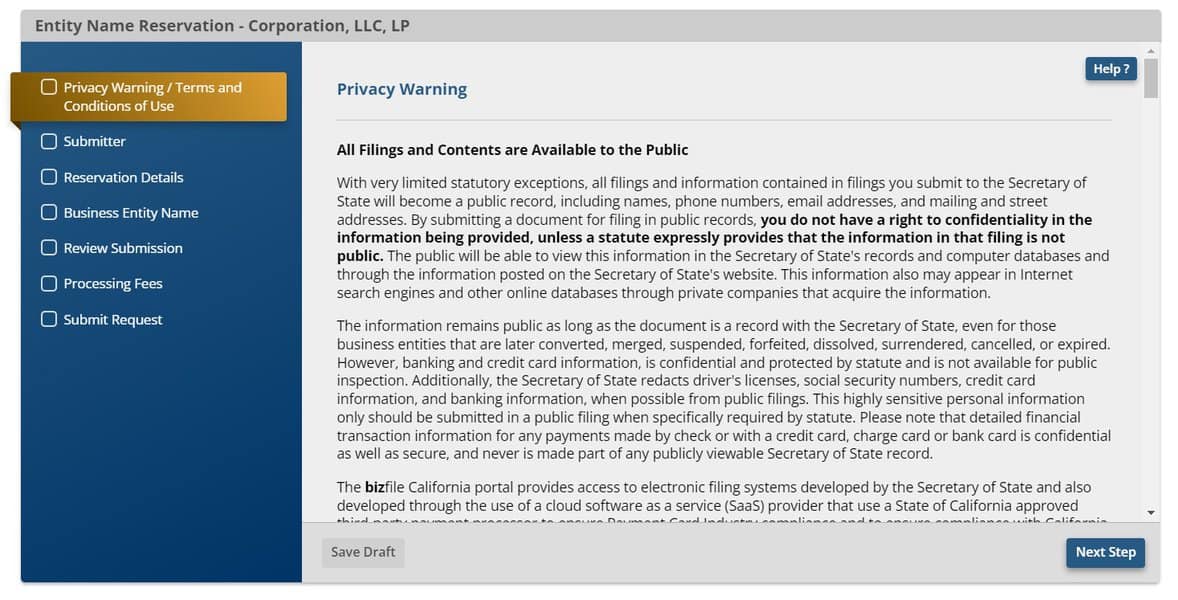
Once you’ve created an account and signed in, read and agree to California’s Secretary of State’s privacy warning and terms of use. Then enter your contact information.
Next, you’ll indicate if your LLC’s name has been reserved and fill in the LLC name on the form. You’ll then enter your company’s principal, mailing address, and registered agent information.
Then you’ll enter your management structure information.

You’ll be allowed to review all your information before payment.
Normally, the filing fee is $70, but it’s $0 until June 30, 2023. You should receive confirmation in five business days if you file online. The turnaround time for filing by mail can be up to two weeks.
Contact Information for the California Secretary of State
California’s Secretary of State Website
California Secretary of State
Business Programs Division
1500 11th Street
Sacramento, CA 95814
916.653.6814
5. Draft an Operating Agreement
An Operating Agreement is a legal document that outlines the ownership and member duties of your Limited Liability Company (LLC).
California LLCs are required to have an Operating Agreement, which can be either oral or documented in writing. If the agreement is written, it’s important to maintain it, including any changes made to it, within the company’s official records.
Here are the elements an LLC Operating Agreement should typically include:
- LLC’s name and principal address (primary location where business is registered)
- Duration of the LLC
- Registered agent name and address
- Membership Information
- Management and voting
- Financial matters (e.g. the way profits and losses will be divided)
- Changes and amendments (e.g. procedures for adding or removing members)
- Disputes, legalities, and policies
- Record keeping and communication
You can find operating agreement templates online, but it’s best to have them drawn up or reviewed by an attorney. The language of an operating agreement is crucial and can often help determine how member disputes will be resolved. For more information about the operating agreement, refer to our comprehensive guide on the California LLC operating agreement, and you can also obtain a free template.
6. Get Your Employer Identification Number (EIN)
The IRS uses an EIN to identify your company for tax filing purposes. An EIN is required if your LLC has more than one member or if you are hiring employees.
Obtaining an EIN requires applying on the IRS website, as detailed here:
All EIN applications (mail, fax, electronic) must disclose the name and Taxpayer Identification Number (SSN, ITIN, or EIN) of the true principal officer, general partner, grantor, owner, or trustor. This individual or entity, which the IRS will call the ‘responsible party,’ controls, manages, or directs the applicant entity and the disposition of its funds and assets. Unless the applicant is a government entity, the responsible party must be an individual (i.e., a natural person), not an entity.
Learn how to get a California Tax ID (EIN) for an LLC.
7. Obtain Business Licenses and Permits
Depending on the nature of your business, you may need to apply for various licenses and permits at the federal, state, and local levels.
At the federal level, licenses and permits are generally industry-specific and may include health licenses and permits from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Check the SBA guide for specific licenses required for your business.
The California State portal provides state license and permit information.
Through CalGold.ca.gov, you can identify any additional licenses your business may require at the local or state level. The portal will provide the necessary details to apply for these licenses.
You may need a general business license to operate at the state level. If you sell tangible goods or services subject to sales tax, you’ll need a seller’s permit.
Here are some standard licenses and permits you may need:
- Industry-specific licenses for certain professions and industries, such as construction, plumbing, electrical, childcare, food handling, liquor, architecture, and finance
- Building and zoning permits
- Doing business as (DBA) permits using a name other than your LLC.
- Health licenses and permits at federal, state, and local levels
- Fire permits
- Sign permits
This is a very important step in the LLC formation process, so make sure that you check with your state and local government offices to find out all the licenses and permits you need.
You could face steep fines and penalties if you operate without the proper licenses and permits.
It’s a good idea to consult with a business attorney to make sure you’re in full compliance. You can also use a service like MyCorporation to do the research and provide you with all the forms you need to license your business entirely.
8. Determine Your Tax Status
By default, an LLC is a “pass-through” entity, which means the business itself does not pay income taxes. Instead, the business’s profits or losses are passed through to the members’ individual tax returns. The taxes are then paid at each member’s individual tax rate.
- Single-Member LLCs: If the LLC has only one member, it’s taxed like a sole proprietorship by default. This means the income from the LLC is reported on the member’s personal income tax return on Schedule C, and they’re responsible for paying self-employment taxes (Social Security and Medicare taxes) on that income.
- Multi-Member LLCs: If the LLC has more than one member, it’s taxed as a partnership by default. The LLC must file an informational tax return (Form 1065), but the income and deductions are passed through to the members. Each member reports their share of the income and deductions on their personal tax return. As with single-member LLCs, members must also pay self-employment taxes on their share of the profits.
An LLC can also choose to be taxed as a corporation by filing an election form with the IRS (Form 8832 for a C-Corp and Form 2553 for an S-Corp). This can be beneficial under certain circumstances:
- C-Corporation Taxation: Electing to be taxed as a C-Corporation can offer benefits to an LLC, particularly if the members want to retain earnings in the company. The corporation pays tax on its profits at the corporate rate (which was 21% as of 2022). If the profits are distributed to the members as dividends, the members must report these dividends on their tax returns and pay tax on them. This is known as “double taxation.” However, members aren’t subject to self-employment taxes on their dividends.
- S-Corporation Taxation: Choosing S-Corporation status can also be beneficial for an LLC. Under this scenario, the LLC does not pay corporate income tax. Instead, the income, deductions, and credits pass through to the shareholders, who report them on their individual tax returns. However, unlike a standard LLC, an S-Corp is required to pay its members a “reasonable” salary for the work they perform for the company. This salary is subject to payroll taxes, but any additional profits distributed to the members aren’t subject to self-employment taxes. This can result in significant tax savings, especially for businesses with high net income.
Other Requirements
Open Your Business Bank Account
When you have an LLC, it’s important to keep your business and personal finances separate for accounting and tax purposes. Commingling your business and personal funds can threaten your liability protection since the line between business and personal assets will not be clear.
Most banks offer business bank accounts, so check with your local bank. You’ll need your EIN and a copy of your Articles of Organization. Your bank may require other documents as well.
Apply for a Business Credit Card
A business credit card can help establish business credit so that if you apply for a business loan or line of credit in the future, you’ll have a better chance of getting approved. A business credit card can also help pay startup expenses, reducing out-of-pocket costs.
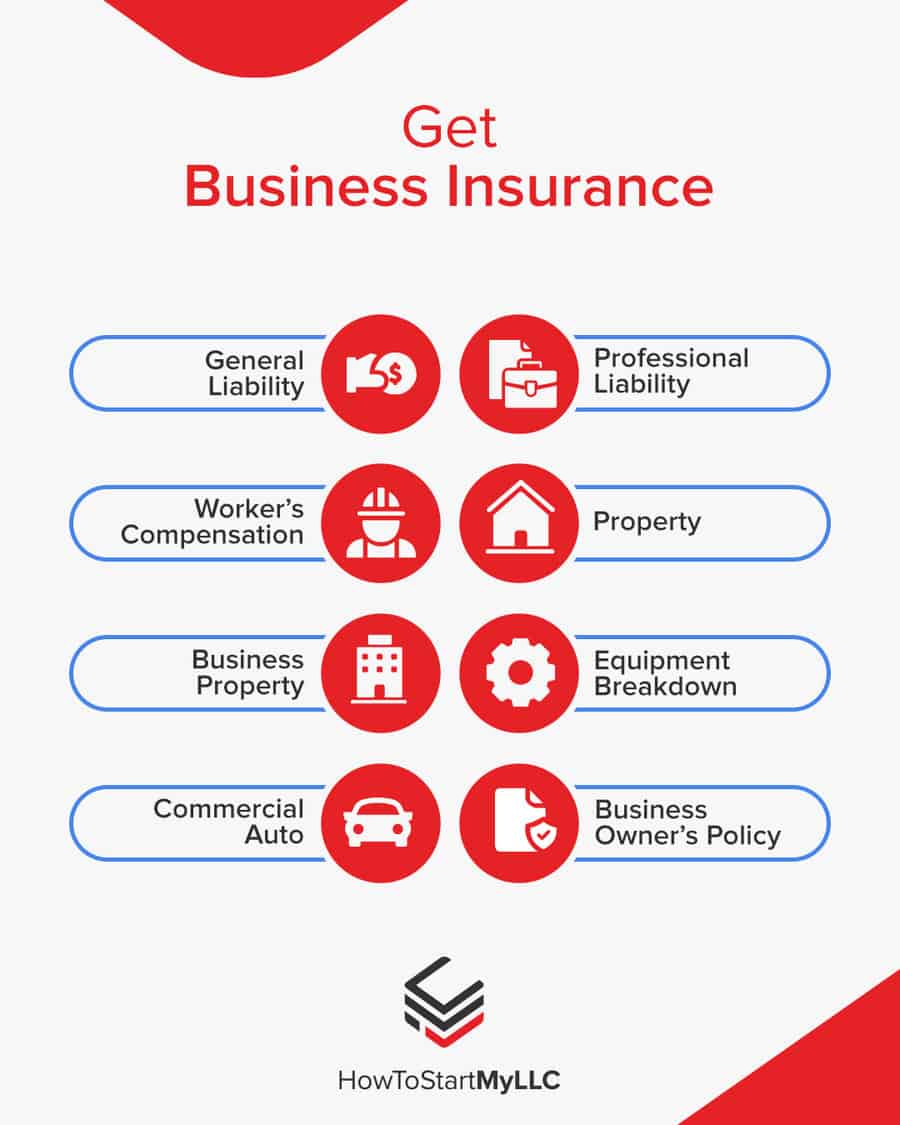
Get Business Insurance
Insurance is the right choice to protect the investment you’ve made in your business. There are several different types of insurance you may need.
- General liability: A comprehensive type of insurance covering many business elements. It includes coverage against bodily injury and property damage.
- Professional liability: Protects against claims from a customer who suffered a loss due to an error or omission in your work. It’s also known as errors and omissions (E&O) insurance.
- Workers’ compensation: Provides compensation to employees injured on the job.
- Property: Covers your physical business space.
- Business Property: Covers equipment and supplies.
- Equipment Breakdown Insurance: Covers the repair or replacement of broken equipment due to mechanical issues.
- Commercial auto: Covers your company-owned vehicles.
- Business owner’s policy (BOP): This option combines the above insurance types.
LLC Records
You’ll want to keep copies of your formation documents and operating agreement in a safe place. Any other official documents, such as vendor contracts and legal or financial documents, should also be kept in your records.
Annual Reporting (Statement of Information)
LLCs in California need to file a statement of information within 90 days of formation and then every two years to remain in good standing, and the filing fee is $20. You can find the form here.
LLCs must also pay an $800 annual tax, due on the 15th of the fourth month after LLC formation and on the 15th of the fourth month of your tax year after that. Here you can find more details on an annual tax and how to pay it.
If your LLC will make more than $250,000, you will have to pay a fee. LLCs must estimate and pay the fee by the 15th day of the 6th month, of the current tax year.
How Much Does it Cost to Start an LLC in California?
| Requirement | Cost |
|---|---|
| Name Reservation Fee | $10 |
| LLC Registration Fee | Currently no fee |
| Business License Fees | Vary by localities and type of business |
| DBA fee | Varies by county |
| Annual Report Fee | $20 plus an $800 annual tax |
